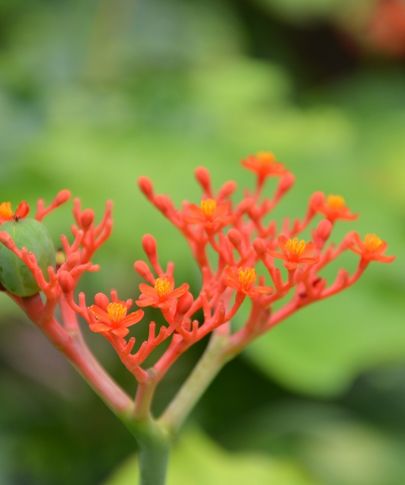
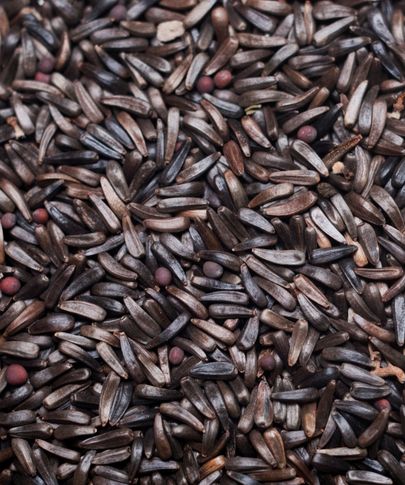
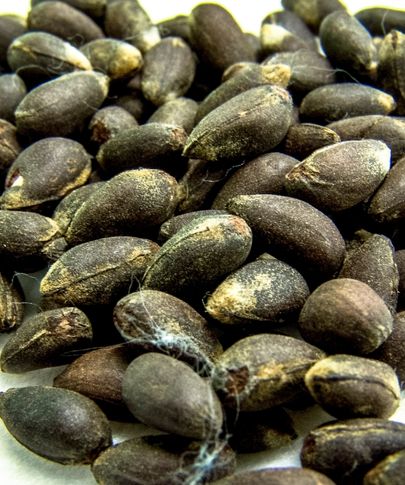
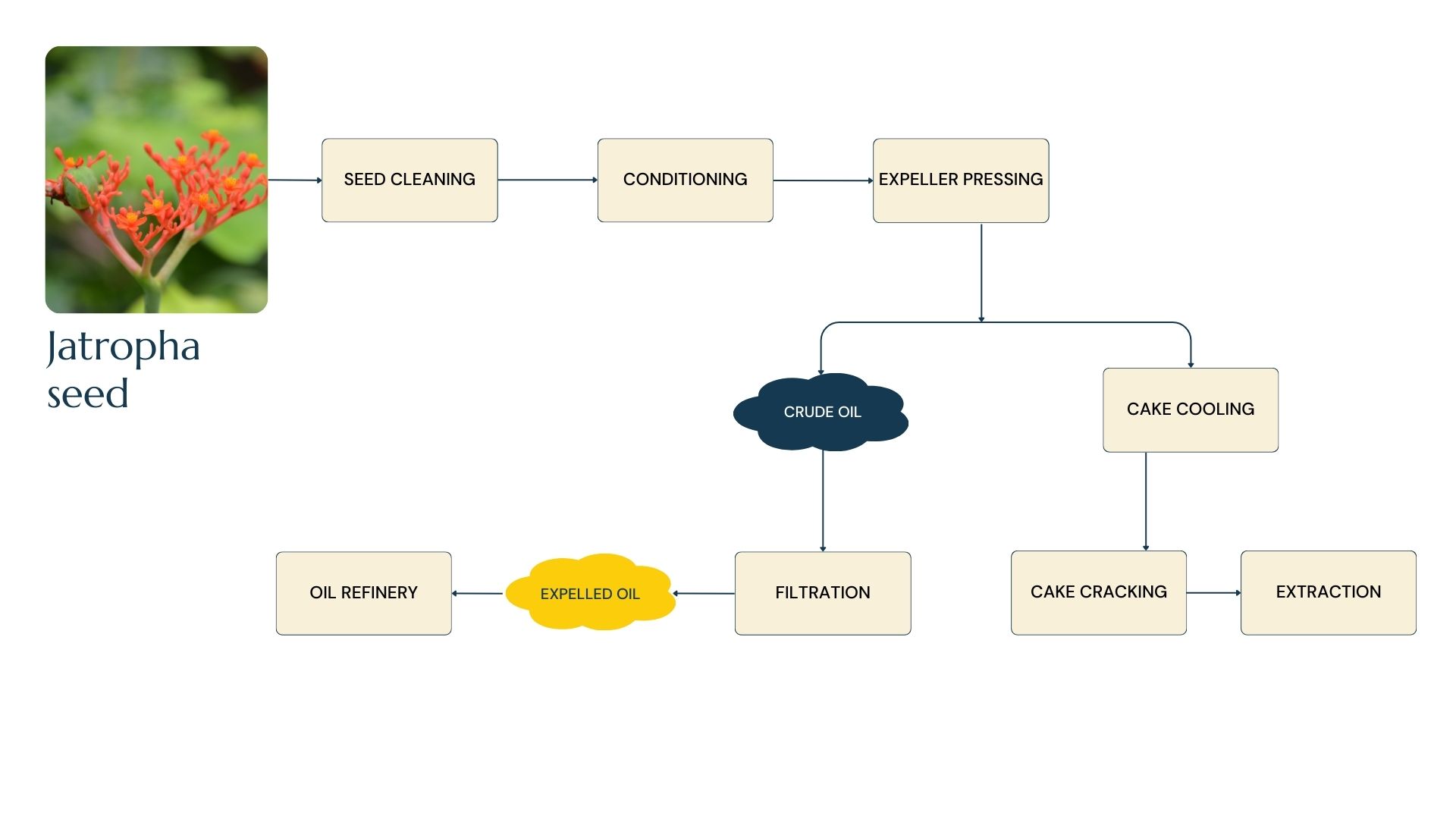
Jatropha seeds come from the hardy shrub Jatropha curcas, known for its ability to thrive in marginal and arid soils. The seeds contain around 30–40% oil, which can be extracted for biodiesel production. Jatropha oil is non-edible due to toxic compounds but is highly valued as a renewable energy source. Beyond biofuel, the seed cake left after oil extraction can be used as organic fertilizer or, after detoxification, as animal feed. This drought-resistant plant can be grown on degraded land, making it a promising candidate for sustainable energy crops without competing directly with food production.
Countries like India, Indonesia, and several African nations have invested in large-scale Jatropha cultivation for energy security. Interest in Jatropha seeds reflects the growing shift towards low-carbon, eco-friendly fuels. While commercialization challenges remain, Jatropha continues to be researched as a reliable feedstock for future energy needs.